In the world of modern manufacturing, blow molding stands as a cornerstone technology that has revolutionized the production of plastic containers and other hollow objects. This article delves into the intricate science behind blow molding, exploring its processes, applications, and significant impact on various industries.
What is Blow Molding?
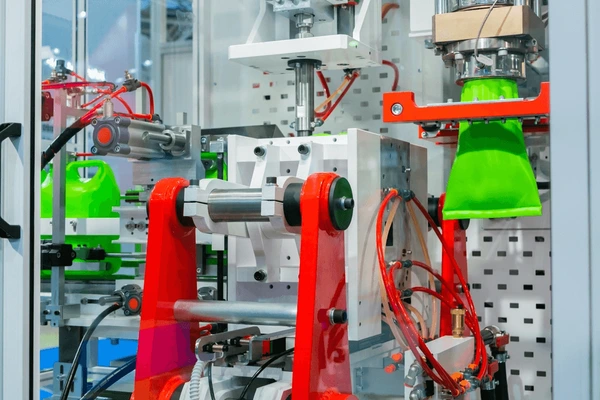
Blow molding is a manufacturing process used to create hollow objects by inflating a heated plastic tube (also known as a parison) inside a mold cavity. This technique allows for the production of a wide range of products, from simple bottles to complex automotive components. The process typically involves three main types: extrusion Blow Molding, injection blow molding, and stretch blow molding, each suited for different applications depending on the desired product specifications.
The Process Explained
Extrusion Blow Molding: This method begins with melting plastic resin to form a continuous tube (parison). The parison is then clamped into a mold cavity, where compressed air is injected to expand the plastic against the mold walls, taking its shape.
Injection Blow Molding: Utilized primarily for small, complex-shaped objects, injection blow molding starts with injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity to form a preform. The preform is then transferred to a blow mold where it is inflated and cooled.
Stretch Blow Molding: Commonly used for producing PET bottles, stretch blow molding involves stretching a preform biaxially and then blowing it into the shape of the mold using compressed air.
The Role of Materials and Design
The success of blow molding relies heavily on the choice of materials and the design of molds. Plastics used in blow molding must possess specific characteristics such as good melt strength, elasticity, and resistance to environmental factors like heat and chemicals. Mold design plays a crucial role in determining the final shape, texture, and thickness of the product, impacting its functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Applications across Industries
Blow molding finds applications across various industries:
Packaging: Plastic bottles, containers, and jars for food, beverages, and personal care products.
Automotive: Air ducts, fuel tanks, and automotive components.
Medical: IV bottles, containers for pharmaceuticals, and medical device components.
Consumer Goods: Toys, storage tanks, and household items.
Environmental Considerations
While blow molding has enabled efficient mass production, its environmental impact is a subject of concern. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices by using recyclable materials, improving energy efficiency, and reducing waste through innovative designs and processes.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in blow molding technology continue to drive innovation in manufacturing. Robotics and automation have optimized production processes, ensuring precision and consistency in product quality. Furthermore, research into biodegradable and compostable materials aims to mitigate environmental impact further.
Blow molding remains a pivotal technology in modern manufacturing, facilitating the production of diverse plastic products essential to daily life. Its evolution continues to be shaped by advancements in materials science, design engineering, and environmental sustainability efforts. As industries seek more sustainable solutions, the future of blow molding lies in its ability to adapt and innovate, meeting the demands of both manufacturers and consumers in an increasingly eco-conscious world.